As it has with every recent version of Windows Server, Microsoft upped the security capabilities of Windows Server 2022 to keep this important infrastructure component protected.
The release of Windows Server 2022 ushered in several important security enhancements. While there is no dictate that states organizations should upgrade to Windows Server 2022 before support ends for older Windows Server versions, it’s a good idea to consider a Windows Server 2022 migration, particularly for critical infrastructure such as domain controllers. A Windows Server 2022 upgrade brings the advantage of security features that do not exist in earlier Windows Server versions. Given the sensitive nature of domain controllers and other infrastructure components in the data center, it makes sense to harden those servers to the greatest extent possible by using Microsoft’s newest server operating system.
Enhancements to Windows Server baseline security
One tool offered to administrators to harden the Windows environment is the Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit, which contains the Windows Server 2022 security baseline, consisting of Group Policy Objects (GPOs) configured according to Microsoft’s recommended best practices. The toolkit includes a Policy Viewer utility to compare a system’s configuration against the baseline security settings.
The Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit is not a new tool, but Microsoft has made some changes to the baselines for Windows Server 2022. For example, the domain controller browser restriction list shows Internet Explorer because Edge is Microsoft’s recommended browser. Similarly, the Windows Server 2022 security baseline now treats script scanning as a security best practice. Microsoft has also made it a best practice that only administrators should be able to install print drivers.
Getting started with the Windows Server 2022 security baselines
To get started, you will need to visit the Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit page and download the Policy Analyzer and the Windows Server 2022 security baseline as .zip files that you will need to extract.
To compare a Windows Server 2022 system against the security baseline, run the PolicyAnalyzer.exe file. Once the interface opens, click on the Add button and then follow the prompts to open the Policy File Importer. Now, select the Add Files From GPOs option from the File menu, as shown in Figure 1.
The Policy File Importer will now display the available GPOs, as shown in Figure 2. The GPOs are role specific. For example, there are GPOs for a general purpose, but there are different GPOs for domain controllers, which need to be hardened to a greater degree than basic servers.
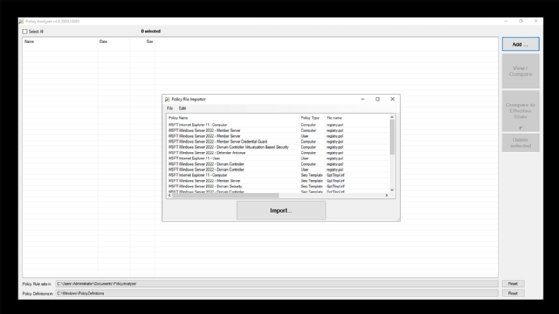
Choose the policy file to use and then click the Import button. When prompted, save the imported GPO as a policy rules file. If you want to compare the baseline against a server’s current state, then click the View/Compare button. This opens the Policy Viewer to compare the baseline against the system’s effective state, as shown in Figure 3.
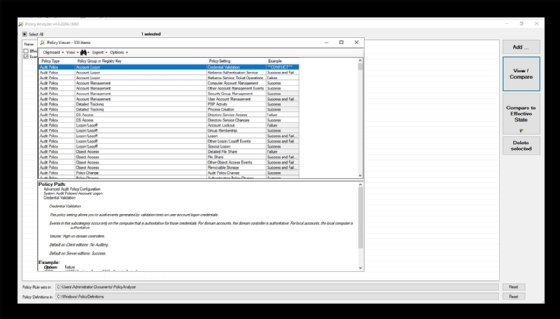
During its comparison test, the Policy Analyzer will highlight the differences between the security baseline and the current system GPOs. The tool will also check for unnecessary or conflicting settings. Administrators can export their findings in Excel format and make a snapshot to check for modifications at another time.
You can find more details about Windows Server 2022 security baselines at the following link.
What tools can help with Windows Server 2022 security hardening?
Microsoft introduced several security features in Windows Server 2022, including the following:
- Secured-core server. Windows Server 2022 supports the use of secured-core hardware, which stores cryptographic keys inside the CPU rather than in a separate Trusted Platform Module (TPM) chip. This greatly improves the security of the keys by making them much more difficult to access, even if an attacker has physical possession of the machine.
- Hardware root-of-trust. Windows Server 2022 uses TPM 2.0 in either the motherboard or on newer processors to implement its Secure Boot feature to check for unauthorized code before loading the operating system.
- Firmware protection. Traditionally, antimalware software cannot scan system firmware. If a server is equipped with a secured-core processor, it can verify the boot process through dynamic root of trust for measurement technology. It is also possible to isolate drivers using Direct Memory Access protection.
- UEFI Secure Boot. With this feature, the system will only boot firmware and operating system files that are trusted by the server’s manufacturer to protect against rootkit attacks.
- Virtualization-based security. This security feature stores credentials and keys in a secure container that the OS cannot access directly to prevent a breach in the event of a malware attack.
- HTTPS and Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.3 enabled by default. Microsoft enabled HTTPS and TLS 1.3 by default in Windows Server 2022 to replace older, less secure protocols. Admins might need to configure applications or services to use it.
- Secure DNS. This feature, also known as DNS-over-HTTPS, encrypts DNS queries to improve privacy by securing traffic to prevent network eavesdropping.
- SMB East-West Encryption. This feature scrambles communications within Storage Spaces Direct clusters to protect the transfer of data between servers.
- SMB Direct and RDMA Encryption. The SMB Direct feature for high-speed transfers in file servers now supports encryption. Windows Server 2022 performs encryption before data placement for much better performance compared to earlier manifestations of this technology.
- SMB Over QUIC. This feature, combined with TLS 1.3, uses a relatively new transport protocol to for data to be securely accessed without the need for a VPN. This feature is only available in the Windows Server 2022 Datacenter Azure Edition.
Windows Server 2022 security hardening best practices
When securing a Windows Server, it is important to remember to practice Defense in depth. The idea behind this concept is that no security mechanism is without its weaknesses, so it is better to create a layered approach that utilizes a variety of security features.
The Security Compliance Toolkit helps to check system settings, but there are some further actions administrators should investigate for additional server security. For example, you might consider using Just Enough Administration and domain isolation policies. Whenever possible, it is also a good idea to configure Windows Servers to run in server core mode.
Finally, each Windows Server should be dedicated to a specific purpose. Running multiple roles or applications on a single server can cause unintended permission elevations that may compromise your security.



